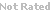 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...- Home
- Molecular Target
- Nuclear Receptor
- ER
- Zearalenone (Toxin F2) | ER agonist
Product Description
Zearalenone is a heat-resistant mycotoxin produced by fungi in food and animal feeds [1]. It acts as an estrogen receptor agonist and can cause hormonal effects in animal species such as the pig [2]. Evidence for Zearalenone effects have been observed in a wide variety of animals. The association between Zearalenone exposure and human diseases remains speculative at present; it has been considered as a possible causative agent in outbreaks of precocious pubertal changes in young children and has been suggested to have a possible involvement in human cervical cancer. [3,4]
Technical information:
| Chemical Formula: | C18H22O5 | |
| CAS #: | 17924-93-4 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 318.36 | |
| Purity: | > 98% | |
| Appearance: | Off-white | |
| Chemical Name: | (3S,?11E)-?3,?4,?5,?6,?9,?10-?hexahydro-?14,?16-?dihydroxy-?3-?methyl-?1H-?2-?benzoxacyclotetradecin-?1,?7(8H)-?dione | |
| Solubility: | Up to 50 mM in DMSO | |
| Synonyms: | Zearalenone, Mycotoxin F2, FES, Zenone, Toxin F2 |
Shipping Condition: The product is shipped in a glass vial at ambient temperature.
Storage condition: For longer shelf life, store solid powder or DMSO solution at -20oC desiccated.
Reference:
| 1. | Zinedine A, et al. Review on the toxicity, occurrence, metabolism, detoxification, regulations and intake of zearalenone: An oestrogenic mycotoxin. Food Chem Toxicol, 2007; 45:1-18 Pubmed ID: 17045381 |
| 2. | Tiemann U. and Dänicke S. In vivo and in vitro effects of the mycotoxins zearalenone and deoxynivalenol on different non-reproductive and reproductive organs in female pigs: A review.Food Addit Contam, 2007; 24:306-314 Pubmed ID: 17364934 |
| 3. | Caloni F. and Cortinovis C. Effects of fusariotoxins in the equine species. Vet J, 2010; 186:157-161 Pubmed ID: 19837621 |
| 4. | Massart F. and Saggese G. Oestrogenic mycotoxin exposures and precocious pubertal development. Int J Androl, 2010; 33:369-376 Pubmed ID: 17364934 |
Other Information:
Product Specification (pdf)
MSDS (pdf)
Certificate of Analysis is available upon request.