 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...- Home
- Disease Area
- Cardiovascular & Metabolic
- SRT1720 | SIRT inhibitor
Product Description
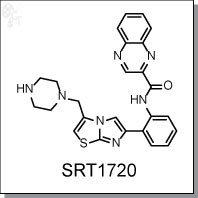
SRT1720 is a selective activator of human SIRT1 (0.16 µM and 781%) versus the closest sirtuin homologues, SIRT2 and SIRT3. It binds to the SIRT1 enzyme-peptide substrate complex at an allosteric site amino-terminal to the catalytic domain and lower the Michaelis constant for acetylated substrates. In animal studies SRT1720 was found to improve insulin sensitivity and lower plasma glucose levels in fat, muscle and liver tissue, and increased mitochondrial and metabolic function. The claim that SRT1720 is a SIRT1 activator has been questioned and further defended since 2007.
Technical information:
| Chemical Formula: | C25H23N7OS C25H23N7OS | |
| CAS #: | 1001645-58-4 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 469.56 | |
| Purity: | >98% | |
| Appearance: | White solid | |
| Chemical Name: | N-(2-(3-(piperazin-1-ylmethyl)imidazo[2,1-b]thiazol-6-yl)phenyl)quinoxaline-2-carboxamide | |
| Solubility: | Up to 100 mM in DMSO |
Shipping Condition: The product is shipped in a glass vial at ambient temperature.
Storage: For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or store DMSO solution at -20oC.
Reference:
| 1. | Milne JC et al. Small molecule activators of SIRT1 as therapeutics for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2007;450(7170):712-6 |
| 2. | Michelle Pacholec et al. SRT1720, SRT2183, SRT1460, and Resveratrol Are Not Direct Activators of SIRT1. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285(30) |
| 3. | Beher D et al. Resveratrol is not a direct activator of SIRT1 enzyme activity. Chem Biol Drug Des 2009. 74 (6): 619–24 |
| 4. | K. Zarse et al. Differential Effects of Resveratrol and SRT1720 on Lifespan of AdultCaenorhabditis elegans. Hormone and Metabolic Research; 2009.42 (12): 837–839 |
| 5. | Dai H et al. "SIRT1 activation by small molecules - kinetic and biophysical evidence for direct interaction of enzyme and activator. J Biol Chem 2010;285 (43): 32695–32703 |
Other Information:
Product Specification (pdf)
MSDS (pdf)