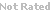 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...- Home
- Stem Cell related
- Pyroxamide | HDAC inhibitor
- Home
- Disease Area
- Oncology
- Pyroxamide | HDAC inhibitor
- Home
- Cellular Mechanism
- Epigenetics
- Histone Deacetylases (HDAC)
- Pyroxamide | HDAC inhibitor
Product Description
Pyroxamide is a potent histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor with IC50 of 100nM. Pyroxamide induced terminal differentiation in murine erythroleukemia (MEL) cells, and inhibited the growth by cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in a variety of tumor cells1-4. An accumulation of acetylated histones and increased levels of p21/WAF1 expression were detected in cancer cells and in prostate xenografts treated with pyroxamide1,2.
Technical information:
| Chemical Formula: | C13H19N3O3 | |
| CAS #: | 382180-17-8 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 265.31 | |
| Purity: | >98% | |
| Appearance: | Off white solid | |
| Chemical Name: | N-Hydroxy-N'-3-pyridinyloctanediamid | |
| Solubility: | Up to 50 mM in DMSO |
Shipping Condition: The product is shipped in a glass vial at ambient temperature.
Storage: For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or store DMSO solution at -20oC.
Reference:
| 1. | Butler et al. Inhibition of transformed cell growth and induction of cellular differentiation by pyroxamide, an inhibitor of histone deacetylase. Clin.Cancer Res. 7 962. (2001) |
| 2. | Kutko, MC., et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce growth suppression and cell death in human rhabdomyosarcoma in vitro. Clin Cancer Res. Nov 15;9(15):5749-55.(2003) |
| 3. | Kouraklis G, Theocharis S. Histone deacetylase inhibitors and anticancer therapy. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. Jul;2(4):477-84.(2002) |
| 4. | Kouraklis G, Theocharis S Histone deacetylase inhibitors: a novel target of anticancer therapy (review). Oncol Rep. Feb;15(2):489-94. (2006) |
Other Information:
Product Specification (pdf)
MSDS (pdf)