 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...- Home
- Stem Cell related
- Kartogenin | Chondrocyte differentiation
Product Description
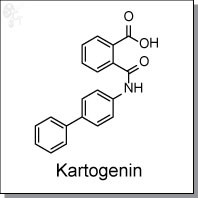
Kartogenin was shown to promote robust chondrocyte differentiation from primary human mesenchymal stem cells/MSCs [EC50 = 100 nM]. Kartogenin-induced chondrocytes from hMSCs express typical set of chondrogenic genes, form chondrocyte nodules, and exhibit characteristic chondrocyte functions. In an in vitro model mimicking cytokine-induced damage during osteoarthritis (OA), 1-5 µM of Kartogenin treatment inhibited nitric oxide (NO) and glycosaminoglycans (GAG) release. Direct Intra-articular (IA) administration of Kartogenin promoted cartilage repair in collagenase and surgery induced OA models in mice, and alleviated OA-induced joint pain. Mechanism of action studies showed that Kartogenin interacts with filamin A (FLNA) and results in the release of transcription factor CBFβ to the nucleus to regulate chondrogenic gene expression.
Technical information:
| Chemical Formula: | C20H15NO3 | |
| CAS #: | 4727-31-5 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 317.34 | |
| Purity: | >98% | |
| Appearance: | Off white solid | |
| Chemical Name: | 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-ylcarbamoyl)benzoic acid | |
| Solubility: | Up to 50 mM in DMSO |
Shipping Condition: The product is shipped in a glass vial at ambient temperature.
Storage: For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or store DMSO solution at -20oC.
Reference:
| 1. | Johnson K. et. al. A Stem Cell–Based Approach to Cartilage Repair. Science (2012) April 5. [Epub ahead of print]. |
Other Information:
Product Specification (pdf)
MSDS (pdf)