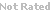 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...- Home
- Disease Area
- Neuroscience
- SPM-927 (Lacosamide)
- Home
- Molecular Target
- Ion Channel
- Na+ Channel
- SPM-927 (Lacosamide)
Product Description
Lacosamide is a small peptide-based agent with a dual mode of action for anticonvulsive and antiepileptic treatment. Lacosamide binds weakly (25-50% inhibition of radioligand binding) to the sodium channel at batrachotoxin site 2. It selectively enhances sodium channel slow inactivation with no effects on fast inactivation. This slow mode of action can lead to normalization of activation thresholds and a reduced pathophysiological hyperresponsiveness. Lacosamide was also shown to be a binding partner to collapsin-response mediator protein 2 (CRMP-2 or DRP-2) with a binding affinity of 5 uM. [1]
Extensive binding studies have shown that Lacosamide and its metabolites do not significantly bind to any of the known binding sites of other anticonvulsant or analgesic agents. Furthermore, it experiences no uptake or metabolism in major neurotransmitters. [2]
Lacosamide is also being studied in animal models of pain and inflammation.
Technical information:
| Chemical Formula: | C13H18N2O3 | |
| CAS #: | 175481-36-4 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 250.29 | |
| Purity: | >98% | |
| Appearance: | White | |
| Chemical Name: | (2R)-2-(Acetylamino)-3-methoxy-N-(phenylmethyl)propanamide | |
| Solubility: | Up to 22 mM in DMSO | |
| Synonyms: | SPM-927, SPM927, Lacosamide, Erlosamide, Harkoseride, Vimpat |
Shipping Condition: The product is shipped in a glass vial at ambient temperature.
Storage condition: For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or store DMSO solution at -20oC.
Reference:
| 1. | Beyreuther et al., Lacosamide: a review of preclinical properties. CNS Drug, 2007, 13(1), 21-42. Pubmed ID: 17461888 |
| 2. | Kellinghaus et al., Lacosamide as treatment for partial epilepsy: mechanisms of action, pharmacology, effects, and safety. Therapeut. Clin. Risk Mgmt. 2009, 5, 757-766. Pubmed ID: 19816574 |
Other Information:
Product Specification (pdf)
MSDS (pdf)
Certificate of Analysis is available upon request.