 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...- Home
- Disease Area
- Oncology
- Cisplatin | DNA crosslinker
- Home
- Cellular Mechanism
- DNA Damage & Repair
- Cisplatin | DNA crosslinker
Product Description
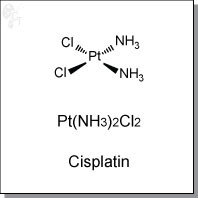
Cisplatin is an intravenously-administered platinum complex that induces cytotoxicity by interference with transcription and/or DNA replication mechanisms. Cisplatin bind preferentially to guanine, and damages tumors via induction of apoptosis. [1] DNA binding proteins recognize the topological distortion of DNA and initiate DNA damage repair, and if repair is not possible, apoptosis.
DNA adducts induced by cisplatin result in activation of several signal transduction pathways, such as ATR, p53, p73, and MAPK, leading to apoptosis. [2]
NSCLC and colon cancers are resistant to cisplatin, while others such as ovarian cancer acquire resistance over time. [3]
Technical information:
| Chemical Formula: | H6Cl2N2Pt | |
| CAS #: | 15663-27-1 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 301.1 | |
| Purity: | >98% | |
| Appearance: | Yellow | |
| Chemical Name: | cis-Diammineplatinum(II) dichloride, cis-Dichlorodiammine platinum(II), cis-Platinum(II) diammine dichloride, Cisplatin | |
| Solubility: | Up to N/A in DMSO | |
| Synonyms: | Cisplatin, Cisplatinum, CDDP |
Shipping Condition: The product is shipped in a glass vial at ambient temperature.
Storage condition: For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or store DMSO solution at -20oC.
Reference:
| 1. | Florea et al., Cisplatin as an Anti-Tumor Drug: Cellular Mechanisms of Activity, Drug Resistance and Induced Side Effects. Cancers 2011, 3, 1351-1371. Pubmed ID: ISSN: 2072-6694 |
| 2. | Siddik et al., Cisplatin: mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene, 2003, 22, 7265-7279. Pubmed ID: 14576837 |
| 3. | Alderden et al., J. Chem. Ed. 2006, 83(5), 728-734. |
Other Information:
Product Specification (pdf)
MSDS (pdf)
Certificate of Analysis is available upon request.