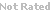 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...- Home
- Disease Area
- Oncology
- CP-358774 (Erlotinib, OSI-774) | EGFR inhibitor
- Home
- Molecular Target
- Tyrosine Kinase
- EGFR/HER Family
- CP-358774 (Erlotinib, OSI-774) | EGFR inhibitor
Product Description
Erlotinib is an orally-available, ATP-competitive, aminoquinazoline-based inhibitor of EGFR at an IC50 of 2 nM. EGFR autophosphorylation is inhibited by Erlotinib at 20 nM. [1]
In DiFi human colon cells, Erlotinib inhibits proliferation at submicromolar concentrations and also blocks the cell cycle in G1, resulting in significant accumulation of the cell cycle inhibitor p27KIP1. Erlotinib induces apoptosis in vitro. [2]
Technical information:
| Chemical Formula: | C22H23N3O4.HCl | |
| CAS #: | 183319-69-9, 183321-74-6 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 429.9 | |
| Purity: | >99% | |
| Appearance: | White | |
| Chemical Name: | N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazolin-4-amine hydrochloride | |
| Solubility: | Up to 5 mM in DMSO | |
| Synonyms: | CP-358774, CP358774, Erlotinib, OSI-774, NSC-718781, Tarceva |
Shipping Condition: The product is shipped in a glass vial at ambient temperature.
Storage condition: For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or store DMSO solution at -20oC.
Reference:
| 1. | Moyer et al., Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by CP-358,774, an inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4838-4848. Pubmed ID: 9354447 |
| 2. | Ciardiello et al., A novel approach in the treatment of cancer: targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 2958-2970. Pubmed ID: 11595683 |
Other Information:
Product Specification (pdf)
MSDS (pdf)
Certificate of Analysis is available upon request.