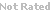 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...- Home
- Cellular Mechanism
- Cell Cycle
- Adriamycin (Doxorubicin) | DNA intercalator
- Home
- Disease Area
- Oncology
- Adriamycin (Doxorubicin) | DNA intercalator
- Home
- Cellular Mechanism
- DNA Damage & Repair
- Adriamycin (Doxorubicin) | DNA intercalator
- Home
- Cellular Mechanism
- Metabolism
- DNA/RNA Synthesis
- Adriamycin (Doxorubicin) | DNA intercalator
Product Description
Adriamycin (Doxorubicin) is an intravenous, anthracycline-based antibiotic and antineoplastic agent derived from Streptomyces bacterium. Adriamycin enters cancer cell DNA and inhibits cell replication by arresting protein synthesis.
In HK-2 cells, adriamycin decreases cell viability in a dose-dependent manner and induces an increase in cells in the sub G1 and G2/M phases. It also increases secretion of TNFa, decreases expression of phosphorylated PKA and Bcl-2, and increases phosphoryled signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, phospho-ERK,and ATF3. [1]
Due to adriamycin's route of administration and cytotoxic effects, extensive research has been conducted in the area of assisted delivery of the chemotherapeutic (liposome [2], prodrug [3], polymer, gold-particles, etc.)
Technical information:
| Chemical Formula: | C27H29NO11.HCl | |
| CAS #: | 25316-40-9 | |
| Molecular Weight: | 579.98 | |
| Purity: | > 98% | |
| Appearance: | Red Orange | |
| Chemical Name: | (8S,10S)-10-((2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yloxy)-6,8,11-trihydroxy-8-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-1-methoxy-7,8,9,10-tetrahydrotetracene-5,12-dione hydrochloride | |
| Solubility: | Up to 100mM in DMSO | |
| Synonyms: | Adriablastin, Adriblastin, Adriblastina, Adriamycin, Doxorubicine, Rubex, Doxorubicinum, Doxorubicina, Doxil |
Shipping Condition: The product is shipped in a glass vial at ambient temperature.
Storage condition: For longer shelf life, store solid powder at 4oC desiccated, or store DMSO solution at -20oC.
Reference:
| 1. | Park et al., Doxorubicin induces cytotoxicity through upregulation of pERK-dependent ATF3. PLoSONE, 2012, 7(9), e44990. Pubmed ID: 23028726 |
| 2. | Macmillan and Cancer Backup factsheet |
| 3. | Albright et al., Matrix metalloproteinase-activated doxorubicin prodrugs inhibit HT1080 xenograft growth better than doxorubicin with less toxicity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 751-760. Pubmed ID: 15897239 |
Other Information:
Product Specification (pdf)
MSDS (pdf)
Certificate of Analysis is available upon request.